 |
�v���g�R�[���W
�@
�P�D �W�{�쐻�C�Œ�
���Œ�g�D�W�{���X���C�h�O���X�ɐڐG�����זE��ڒ�������D
�����Ƀh���C���[�Ȃǂŏ\���ɗ╗�����D
�J���m�A�Œ� �S���C�P�O�`�P�T���D
�╗�����D
�Q�D�W�{�O����
�ώ@�̈���C�_�C�������h�y���Ń}�[�N����D
2XSSC
37���@10��
0.5mg/ml Pepsin 37���@13���i�X�C�ޗ��Œ����j
PBS �@�@�@�@5���i�����j
1��formaldehyde �@5��
PBS �@5��
70 %, 85 %, 100
% Alc. �@�e1��
Air dry
�܂��́C���M�i60���`70���C�Q���ԁj�ɂ��q�[�g�G�[�W���O�D
�R�D�W�{�ϐ�
�\��73���ɉ��������ϐ��n�t���ɕW�{���R���ԁi�X�C�ޗ��Ŕ������j�Z��
70���C85���C100���G�^�m�[���e�P���ԁD
�S�DProbe�����C�ϐ�
Hybridization
Buffer 7��l, �W�I�v���[�u 1��l, ������2��l, ��0.5ml �G�b�y���`���[�u���ō������C�Q�`�R�b�ԉ��S����D
75���E�H�[�^�[�o�X�łT���ԉ������ăv���[�u��ϐ�������D
�X�����ɂċ}��ۑ��D
�T�D�n�C�u���_�C�[�[�V����
37���̃z�b�g�v���[�g�ɕW�{���ڂ���D
�v���[�u�~�b�N�X10��l�Y�����C�J�o�[�K���X�������y�[�p�[�{���h��
�������ɕW�{�����C37���ňꒋ��C���L���x�[�g����D
�U�D���
�y�[�p�[�{���h�����D
45���ɉ����������t1��10���ԁi�J�o�[�K���X�����R����)
45���ɉ����������t2�C3�Ɋe10���Ԑ��D
45���ɉ�������2�~SSC��10���Ԑ��D
2�~SSC��5���Ԑ��D
PN
buffer �łT���Ԑ���C�������łT���Ԑ�y������������D
DAPI�U10 ��l �Y�����C�J�o�[�K���X�������}�j�L���A�ŃV�[��������D
�i�Q�l�jTwo-color FISH�̃v���[�u����
Hybridization
Buffer 7��l
�Z���g�����A�v���[�u�iSpectrum Green�j 1��l
�̈���ٓI�v���[�u(Spectrum Orange) �@ 1��l
������ �@�@
�P��l total 10��l
�@ ���a�C���S��A�ϐ�����D���͓��l�ɍs���D
����
10% �����ɏՃz���}���� 12.5ml
H2O 20ml
�n�C�u���_�C�[�[�V�����n�t
�@�@�z�����A�~�h�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@5.5ml
�@�@���_�f�L�X�g�����@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@1.0g
�@�@20�~SSC �@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@0.5ml
*�S�y���������ߊh�a�ɒ���
���t(pH 7.0)
2�~SSC / 0.1% NP-40 (pH 7.0 )
A�t�F0.1M Na2HPO4 / 0.1% NP-40
B�t�F0.1M NaH2PO4 / 0.1% NP-40
�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@ A�t��B�t�������Ȃ���CpH 8.0�ɒ���
|
|
 Tharmal Cycler���g�p����FISH Tharmal Cycler���g�p����FISH
�P�D�W�{�Œ�
�J���m�A�Œ�
4���@10�`15��
����
�Q�D�W�{�O����
2XSSC
37���@10��
0.5mg/ml Pepsin
37���@13��
PBS �@5��
1��formaldehyde
5��
PBS
5��
70 %, 85 %, 100 %
Alc.
�e1��
����
�R�DDNA�ϐ��ƃn�C�u���_�C�[�[�V����
Thermal cycler�ɕW�{���Z�b�g
���������v���[�u��Y�����J�o�[�K���X���ڂ���
�y�[�p�[�{���h�ŃV�[��������
73���@3���i�ϐ��j�������@37�� �ꒋ��
�i�n�C�u���_�C�[�[�V�����j
�S�D�v�����@
�y�[�p�[�{���h����菜��
2XSSC
5���i�J�o�[�K���X�����j
0.4XSSC/0.3%NP-40 73�� 2��
2XSSC/0.1%NP-40 5�b, - 1��
2XSSC ���
�T�D����F
DAPI�U�@�P�O��l
�i�W�{�����S�Ɋ����O�ɁCDAPI�U��Y�����J�o�[�K���X���ڂ���j
�i�Q�l�jTwo-color FISH�̃v���[�u����
Hybridization Buffer
7��l
�Z���g�����A�v���[�u�iSpectrum Green�j 1��l
�̈���ٓI�v���[�u(Spectrum Orange)
1��l
�@�@����
0.5mg/ml pepsin (pH2.0)
1% formaldehyde
10% �����ɏՃz���}���� 12.5ml
0. 4XSSC/0.3%NP-40
(pH 7.0)
20XSSC 20ml
NP-40 3ml
H2O total 1,000ml
2XSSC/0.1%NP-40 (pH7.0)
20XSSC 100ml
NP-40
1ml
H2O total 1,000ml
|
|
�@�@ FISH on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue section FISH on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue section
�@�@Day 1
�@�@1. 6% neutral-buffred formalin fixation
�@�@2. Paraffin-wax embedment
�@�@3. Prepare 4-6 ��m tissue section slide
�@�@4. Xylene 10 min X3
�@�@5. Ethanol 10 min X2
�@�@6. Microwave-heating for 15 min (0.01M sodium citrate buffer, pH
�@�@�@�@6.0)��H2O (approximate 2 min)��PBS (approximate 2 min)
�@�@7. 0.05%-0.5% pepsin/0.1N HCl at 37�� for 12 min.
�@�@8. H2O (approximate 2 min) X2
�@�@9. 70% Ethanol (2 min)��85% Ethanol (2 min)��100% Ethanol (2 min)��air dry
�@�@10. Preheating of section slide (place the slide on the lid of water
�@�@�@�@bath at 73�� before preparation and denaturation of probe solution)
�@�@11. Prepare probe solution (for example: 7��l hybridization buffer + 1��l
�@�@�@�@probe + 2 ��l DDW for CEP probe, Vysis)
�@�@12. Denature probe solution at 73�� for 5 min then move to 45��
�@�@13. Denature the section in a denaturation solution at 73�� for 5 min.
�@�@14. 70% Ethanol (2 min at -4 to -20��)��85% Ethanol (2 min at -4 to
�@�@�@�@-20��)��100% Ethanol (2 min at -4 to -20��)��air dry
�@�@15. Hybridization at 37���� cover and seal the section with coverslip and
�@�@�@�@rubber cement
�@�@16. Mark on the section slide
�@�@17. Incubation at 37�� for 3 days
�@�@Denaturation solution
�@�@ 7ml 20X SSC
�@�@14ml H2O
�@�@49ml formamide
�@�@Day 4
�@�@1. Remove rubber cement from slide and immerse in 2X SSC/0.3% NP-40 at
�@�@�@�@room for 2-5 minutes.
�@�@2. 2X SSC/0.3% NP-40 at 73�� for 2 minutes
�@�@3. 2X SSC/0.3% NP-40 at room for 1 minute
�@�@4. 70% Ethanol (1 min)��85% Ethanol (1 min)��100% Ethanol (1 min)��air dry
�@�@5. Counterstain and apply coverslip��observation under fluorescence
�@�@�@�@microscope.
�@�@2X SSC/0.3% NP-40
�@�@4ml 20X SSC
�@�@36ml H2O
�@�@120��l NP-40
���̃y�[�W��TOP��
|
�@�@�@ Comparative Genomic Hybridization(CGH) Comparative Genomic Hybridization(CGH)
�E���F�̕W�{�X���C�h�̑O����
�J���m�A�Œ�@ 4���@30��
�����i�������芣�����j
�Q�~SSC �@10���i�G�[�W���O�j
�y�v�V�������@�V���@�@(0.5mg/ml
pepsin pH2.0)�i���ʂ��݂ēK�X�����j
PBS
�T��
�P% formaldehyde
�T��
PBS�@�T��
70%, 80%, 100% �G�^�m�[�� �@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@ �e�P��
����
75���E�H�[�^�[�o�X�̃X�e�����X���W�̏�ɕ��u�@2����
�E����
1% formaldehyde
10%�����ɏ�������@�@�@�@�@ 12.5ml
�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�P�~PBS 37ml
�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�QM�@MgCl2 0.5ml
0.5 mg/ml
pepsin (pH 2.0)
0.01N-HCl �Ŋ�߁@�@ 10%�@�y�v�V���@0.25ml
�@�@�@�@�@�@�@H2O �@ 50ml
1N HCl 500��l
�E�v���[�u�̒P���������i0.5ml�̉��F����ނ��֗��j
�P�j
�v���[�u�̍쐬�i�ォ�珇�Ԃɓ����j
�@�@�@Human COT-1 DNA�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@ 10 ��l
�@�@�@�RM�@�|�_�i�g���E���@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@4.0 ��l
�@�@�@100%�@�G�^�m�[���i�㓙�Ȃ́j
110 ��l
�@�@�@����l�����p��DNA�iSpectrum Red �W���j�@�@�@ 10 ��l
�@�@�@���DNA�iSpectrum Green �W���j
20 ��l
�@�@�ȏ���悭���aނ���B
�Q�j�@�Ռ����ɗe��A�]�|���a���|80���Ɉ�Ӓu���i�P���Ԉȏ�u���j
�R�j�@12000��]4�� 20�����S
�S�j�@�㐴���̂Ă�B
�T)�@�@70% �G�^�m�[����200 ��l����12000��]10��
�U�j�@�㐴���̂āA���r�Ŏc�����������z�����B
�i�����ŁADNA�̔���������r�ɂ������Ȃ��l�ɋC������B�Ռ����Ȃ��犣�����B�i1 - 2���Ԓ��x�j
�V�j�@Master Mix��10��l�����悭���a����B�Ǖǂɂ���Master Mix��10�b���x���S���ė��Ƃ��B
�W�j�@�R�V���Ŗ�P�O���ۉ��i�Ռ��j
�X�j�@�`���[�u���̃v���[�u���h�a����B
�P�O�j �S�T���ɂP�O�`�P�T���Òu�B
�P�P�j �V�T���ɂU�������B�i��۰�ނ̕ϐ��j
�P�Q�j �R�V���ɂR�O���ȏ�Òu�B
�E���F�̕W�{�̒P��������
�P�j �X���C�h�O���X�i�X���C�h�̗��Ɉ������j��37����10�����炢�u����
�@�@�@75���̏�ɂP���ԁ`�Q���Ԓu���B
�Q�j Denaturing�@Solution�i75���j�ɃX���C�h�O���X���Q���P�O�b�`�Q���R�O�b�i�P�����j
���j�X���C�h�O���X���P�������Ɩ�P��������̂łP�x�ɂQ���ȏ㏈�����Ȃ��B
�R�j�@70�D80�D100 ���G�^�m�[���i�X���j�ɂĂQ���ԂÂE������B
�S�j�@��������B
�T�j�@37���̃z�b�g�v���[�g��ʼn��߂Ă����B
�E�n�C�u���_�C�[�[�V����
�P�j �X���C�h�O���X�Ƀv���[�u��10 ��l�H������B
�Q�j 18�~18mm�̃J�o�[�O���X�ɂĔ킢�A�y�[�p�[�{���h�Ŏ��͂��V�[������B
�R�j 30���ԃz�b�g�v���[�g�i37���j��ɐÒu����B
�S�j 37���̍P�����ɂ�72���ԃn�C�u���_�C�[�[�V��������B
�E���
�P�j �T�O����ѱ���/2�~SSC 45���@�@�U���~�R��
�Q�j �Q�~�r�r�b�@45���@�@ �@�@�@�@�V���~�P��
�R�j �o�m�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@ �@�@�@�@�@ �T���~�P��
�S�j �c�v�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@ �@�@�@�@�@ �T���~�P��
�T�j �������37���̃z�b�g�v���[�g��ɂT���`10���i�������m�F�j
�U�j �c�`�o�h�U 10��l��H�����A18�~18�����̃J�o�[�O���X�������}�j�L���A�ŃV�[������B
������v ���p���[�g���ɓ���퉷�ŕۑ��B
�E����̒���
20�~SSC
�@�@�@�@NaCl�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@43.8���@�@�@�@175.3g
C6H5O7Na3�E2H2O�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@ 22.1���@�@�@�@88.2g
�������@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@200ml�@�@�@�@800ml
���X�A�b�v�p�i�������j�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�{�� �{��
�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@�@250ml 1000ml
�@�@PH���[�^�[��PH��7.0�ɂPN��HCl�ł��킹���̌チ�X�A�b�v�B
�E�ϐ��n�t�iD.S�j100ml
�z�����A�~�h70ml�@�E20�~SSC�i��H7.0�j10ml�@�E������20ml�������ėǂ���������BPH7.0
�ł��邱�Ƃ��m���߂�B
�E�G�^�m�[�����t
��������100���G�^�m�[����p����70���@80���@100���̍ŏI�Z�x�ƂȂ�悤�Ɋ�߂���B
�E�z�����A�~�h���t50
%formamid/2�~SSC
�z�����A�~�h75ml�@20�~SSC(pH7.0)15ml ������60ml��ǂ���������B�����ł�H���[�^�[��p���Ă�H7.0�ɒ�������B3�̃K���X���R�v�����W���[�i1�C2�C3�ƕ\�����āj�ɓ����B
�EPN�@2�~SSC/0.1��NP�|40�i100ml�j
90ml�̏�������20�~SSC�i��H7.0�j��10ml������B0.1ml��NP�\40��������BNaOH�ł�H 7.0�ɒ�������B
|
|
 MicroDissection MicroDissection
PROTOCOL FOR MANUAL TISSUE MICRODISSECTION
This method is applicable to various kinds of cancer tissues to reduce
stromal tissue components from cancer specimens. Investigators should also
expect to invest time initially by practicing on 10 to 20 cases to begin
to feel comfortable with the technique. As they become skilled in the microdissection
technology, they obtain tissue fragments rich in cancer cells in a short
time.
I.
Preparation of frozen tissue sections
1. Set the machine (cryo-stat) for -20��
(It takes at
least a few hours to get the optimal temperature. Fortunately, the machine is
usually maintained at -20C in this laboratory.)
2. Squeeze one drop of OCT compound (Tissue Tek) in bottom of mold, then put
the tissue specimen in the center of it, and full the mold by OCT compound.
(avoid to trapping air bubbles)
*Embed fresh tissues carefully in OCT in plastic mold, taking care not
to trap air bubbles surrounding the tissue. Freeze tissue by setting mold
on top of liquid nitrogen until 70-80% of the block turns white and then
put block on top of dry ice. The frozen blocks may be stored at minus 80��C for long-term�@storage.
3. Put mold in machine for 20-30 minutes.
This process can be omitted, when the tissue specimens
frozen by another method are used.
4. Take out the cylinder from machine and placed
one drop of compound
on up of fit for mold
fixation, Convert the mold and put in top of the
cylinder, leave it for 10
minutes in the machine.
5. Remove mold�fs
frame (plastic).
6. Adjust the
cylinder for tissue sectioning.
7. Cut the tissue
block with a razor at 5��m, and put on the slide
nicety.
(A tissue section is prepared for
microscopic observation. When the density of cancer cells is very low, another
tissue specimen should be used.)
8. Then, section the
tissue block at 30��m.
9. Make totally 12-16 slides with repeat of procedures No. (7 to 8 ).
10. Leave slides in
Ethanol 100% for 5minutes.
11. Stain tissue
sections with HE.
The lower concentration of hematoxylin and eosin may
improve macromolecule recovery.
12. Arrange slides on
the map-wood, and put a cover glass only on 5��m-Sections.
We should evaluate the cancer cell content in the
tissue section before beginning microdissection.
II. Tissue microdissection - Picking up the cancer cells
We perform microdissection on a standard inverted microscope (stereomicroscope)
using a 27 gauge needle on a syringe as the microdissecting tool.
Prepare in advance; �@1.5ml-eppendorfe
tube
�@�@�@�@�@�@�B1ml-syringe with
27G needle
1. At first, spill a little of Ethanol on the
slide, look for cancer cell
nest, and take out that by
needle of syringe, put it in the eppendorf
tube (tube with 1/2 volume
alcohol).
While viewing the tissue
through the microscope, the cell population of interest should be gently
scraped with the needle. (As another way, first stromal tissues are removed
from cancer tissue specimens, and cancer cell populations are left on the
slide.) The dissected cells will become detached from the slide and form small
dark clumps of tissue that can be collected on the needle. Several small tissue
fragments can be procured simultaneously. Collection of an initial fragment on
the tip of the needle will assist in procuring subsequent tissue. The tip of
the needle with the procured tissue fragments should be carefully placed into a
small PCR tube containing ethanol. Gentle shaking of the tube will ensure the
tissue detaches from the tip of the needle.
2. Centrifuge the tube for 5minutes at 14,000rpm.
3. Remove the alcohol only, soak the tissue fragments in PBS, and centrifuge
the tube for 5 minutes at 14,000rpm.
4. Remove PBS.
5. Go to the DNA extraction step (Dneasy tissue kit, QIAGEN, or SepaGene,
Sankojunyaku Co., Ltd.)
DNA EXTRACTION FROM MICRODISSECTED TISSUE SPECIMENS
DNA extraction is performed with a DNA extraction kit according to the
manufacturer�fs instructions. We use two kits (products of Sanko-junyaku
and Quagen) for DNA extraction.
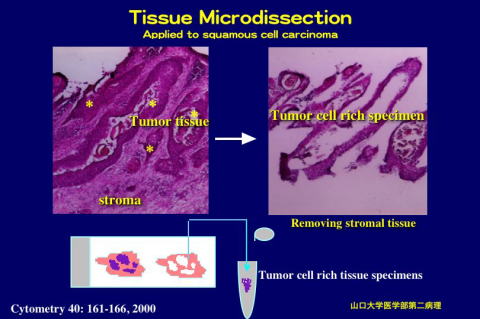
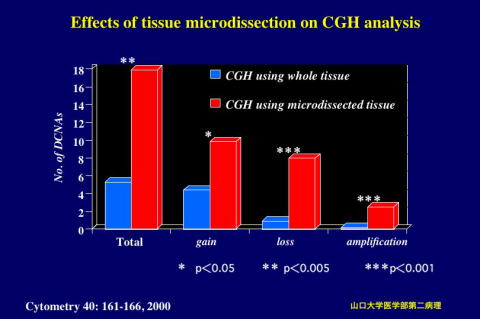
|
|
���̃y�[�W�̃g�b�v��
 Mutiplex-Immunostain chip (M-I chip) Mutiplex-Immunostain chip (M-I chip)
Immunohistochemical examinations that are
inevitable to a precise histopathological diagnosis in pathological
laboratories are time consuming, laborious and expensive. In order to make
immunohistochemical examination efficient, we have developed a novel device
designated as �eMultiplex-Immunostain Chip (MI Chip)�f for immunostaining of
tissue sections and smear preparations. On a plastic plate, there are 50 small
hallows which contain optimally diluted 5��l antibody solution. A tissue section is placed on the plate and fastened
with clips tightly. Then, they are turned upside down, resulting in the
automatic application of antibodies to the section. Since the plate allows
immunohistological staining of 50 different antibodies at the most for
a tissue section in a single experiment, it markedly reduces the time,
effort, and expense to the immunohistochemical examination. In addition,
expensive bioanalytical instruments are unnecessary for it. The chip is
useful for not only histopathological examinations but also genetic studies.
A number of applications of this method can be envisioned in the field
of tumor diagnosis and cell biology.
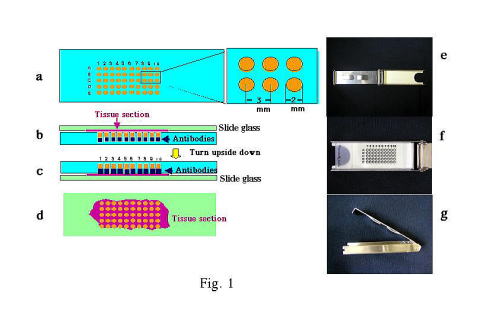
1.jpg)
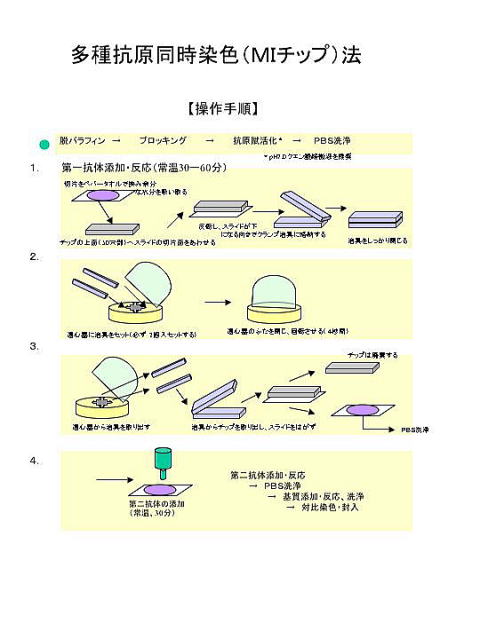
|
|
 |
|